IC
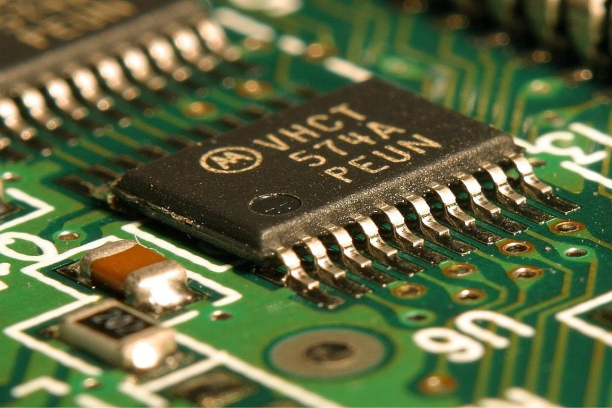
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, electronic integrated circuits, commonly known as ICs, play a pivotal role in powering the devices and systems we use daily. From smartphones and laptops to cars and industrial machinery, ICs are the unsung heroes behind the scenes, enabling the functionalities that have become integral to our lives. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the world of electronic ICs, exploring what they are, how they work, and their significance in modern electronics.
“Electronic Integrated Circuits are the backbone of modern electronics, enabling the incredible technological advancements we experience daily.”
- Analog ICs: These ICs work with continuous signals, typically voltages and currents, to amplify, filter, or manipulate signals. They are commonly used in applications like audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, and sensor interfaces.
- Digital ICs: Digital ICs work with discrete values (0s and 1s) and are essential for digital computing and data processing. They are the building blocks of microprocessors, memory chips, and various digital logic circuits.
The Pioneering Role of Electronic ICs in Revolutionizing Technology
Electronic ICs, or integrated circuits, are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics, packing complex circuitry onto tiny silicon chips to power our devices. These micro wonders enable everything from smartphones to spacecraft, revolutionizing technology and enhancing our daily lives.
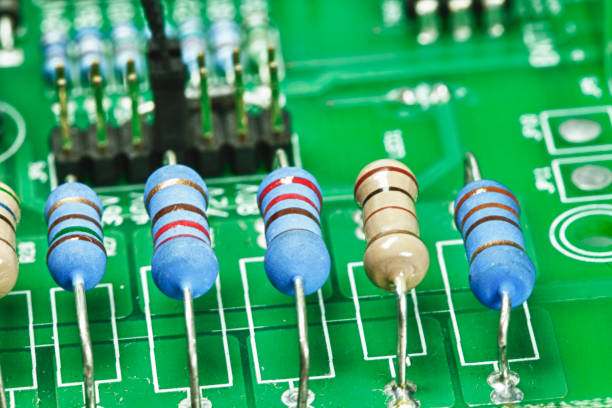
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that resists the flow of electric current. It is designed to create a specific amount of resistance in an electrical circuit, which is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistors are typically constructed as small, cylindrical components with color-coded bands indicating their resistance value and tolerance.
“Electronic resistors are indeed the unsung heroes of electrical engineering.”
- Carbon Composition Resistors: Made from a mixture of carbon and an insulating material, these resistors are cost-effective and widely used in general-purpose applications.
- Film Resistors: Constructed by depositing a resistive film on an insulating substrate, film resistors are available in metal film, carbon film, and thick-film varieties, offering high precision and stability.
- Variable Resistors: Also known as potentiometers or rheostats, these resistors have an adjustable resistance, making them suitable for volume controls and tuning circuits.
- Surface Mount Resistors (SMD): These miniature resistors are designed for automated assembly processes and are prevalent in modern electronics due to their compact size.
LED
In today’s interconnected world, light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, have become a ubiquitous and essential part of our daily lives. From the tiny indicator lights on our devices to the dazzling displays in Times Square, LEDs are illuminating our world in ways we could never have imagined just a few decades ago. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at electronic LEDs, exploring their fascinating history, how they work, and the myriad of ways they are transforming technology and lighting.
“LEDs are, quite literally, lighting up the future of technology and everyday life.”
- Semiconductor Materials: LEDs are typically made from semiconductor materials, such as gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, or silicon carbide. These materials have specific properties that allow them to emit light when electrons and holes recombine within the semiconductor crystal.
- Electron-Hole Pair Formation: When an electric current flows through the LED, it energizes electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to move from the conduction band to the valence band. This process creates electron-hole pairs.
- Recombination and Light Emission: As electrons recombine with holes, they release energy in the form of photons, which are particles of light. The energy level difference between the conduction and valence bands determines the wavelength and color of the emitted light.