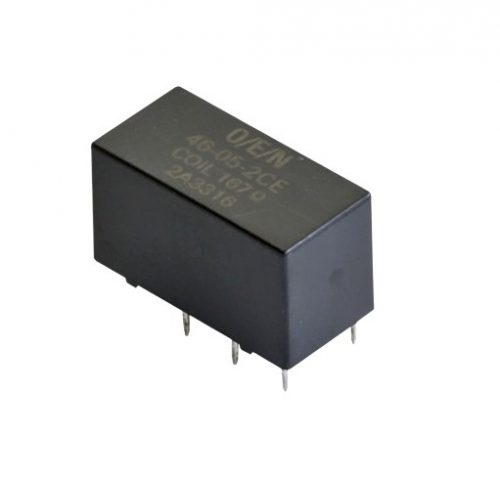






No.1030, Shriram Building,
Near Nagnath Par,
Sadashiv Peth, Pune – 411030,
Maharashtra, India
![]() Visit Our store
Visit Our store
Monday to Saturday
10:00 AM to 7.30 PM
(Store closed on all Sundays and Public Holidays)
*All the prices are excluding Tax rates & are subject to change after a specific period of time.
Copyright © 2024@AbhinavDCS